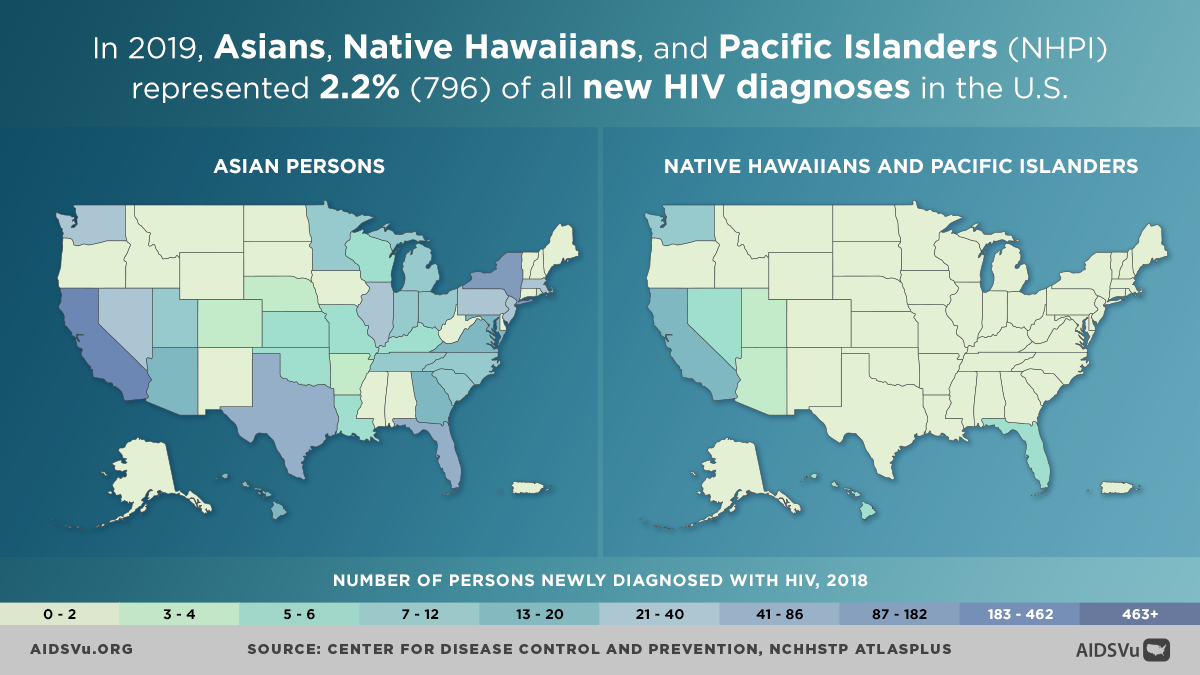
In 2019, Asians, Native Hawaiians, and Pacific Islanders (NHPI) represented 2.2% (796) of all new HIV diagnoses in the U.S. Since 2017, Asians, Native Hawaiians, and Pacific Islanders have seen a downward trend in new HIV diagnoses and experienced a 15% decrease from 2018 to 2019. Despite this decrease, there was an overall 13% increase in new HIV diagnoses among this group from 2008 to 2019.
On this year’s NAPIHAAD, we recognize the impact of social determinants of health and cultural factors such as stigma, language barriers, and discrimination in producing negative HIV-related health outcomes for Asians, Native Hawaiians, and Pacific Islanders. For example:
- In 2018, 13.3% of the U.S. population were living in poverty, compared to the 10.8% of Asian people and 16.7% of Native Hawaiians/Pacific Islanders.
- In the same year, 8.9% of the U.S. population were uninsured, compared to the 6.3% of Asian people and 10.6% of Native Hawaiians/Pacific Islanders.